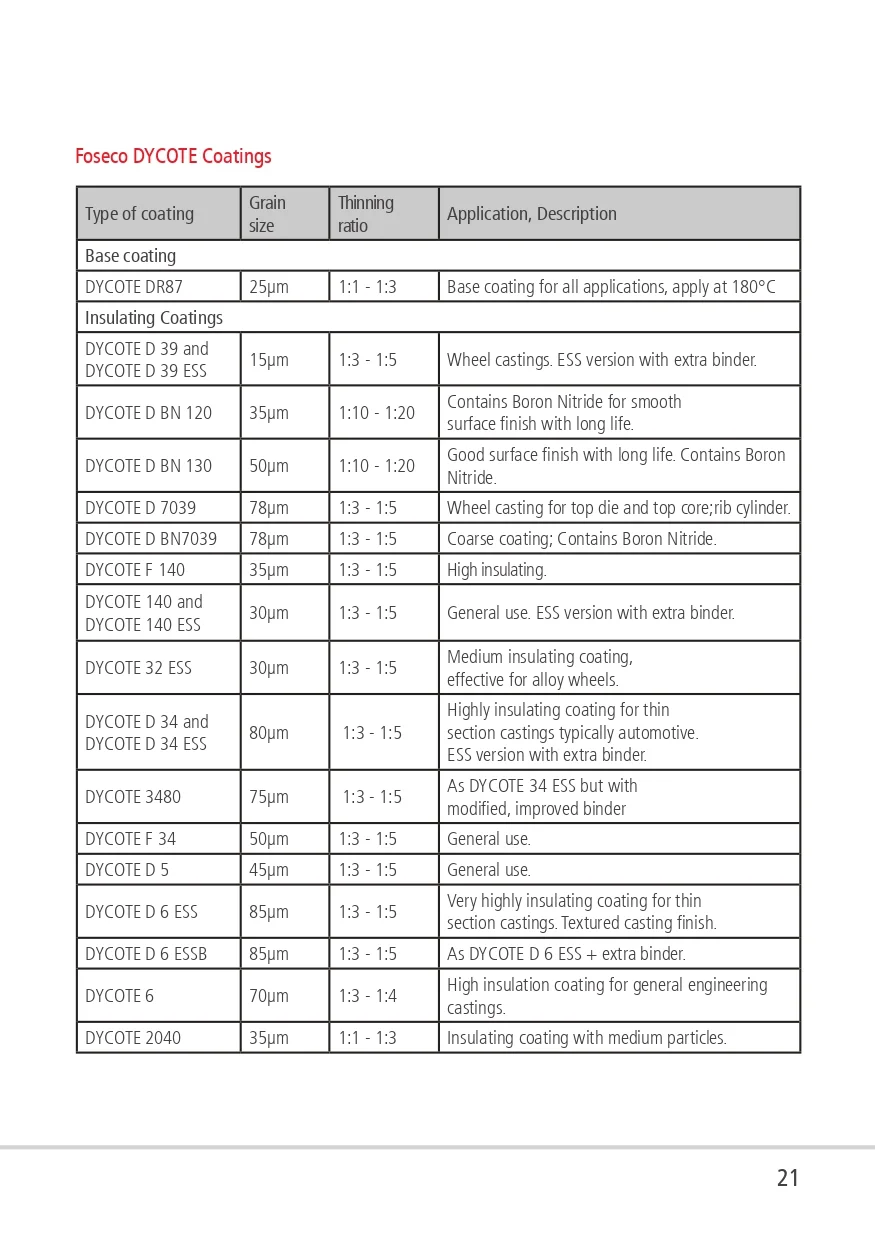
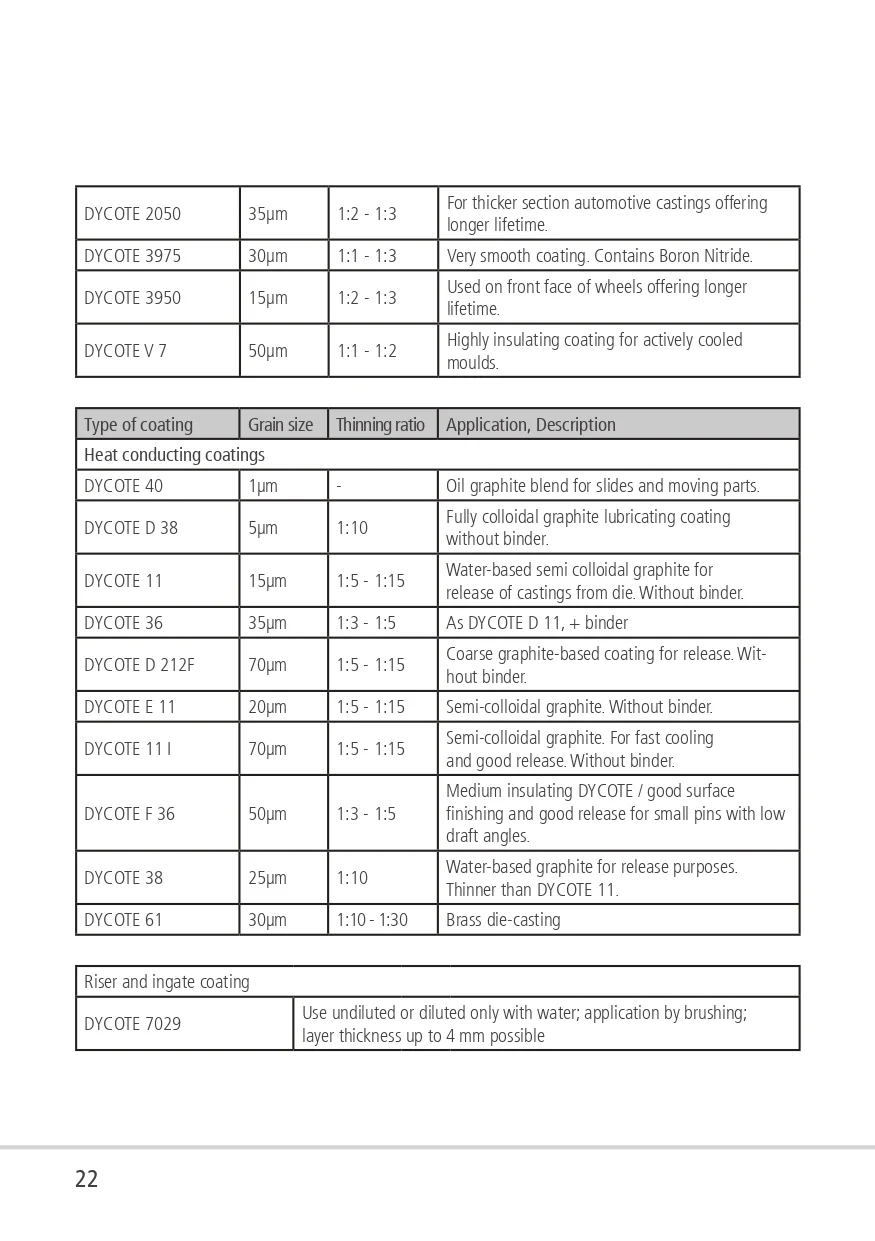
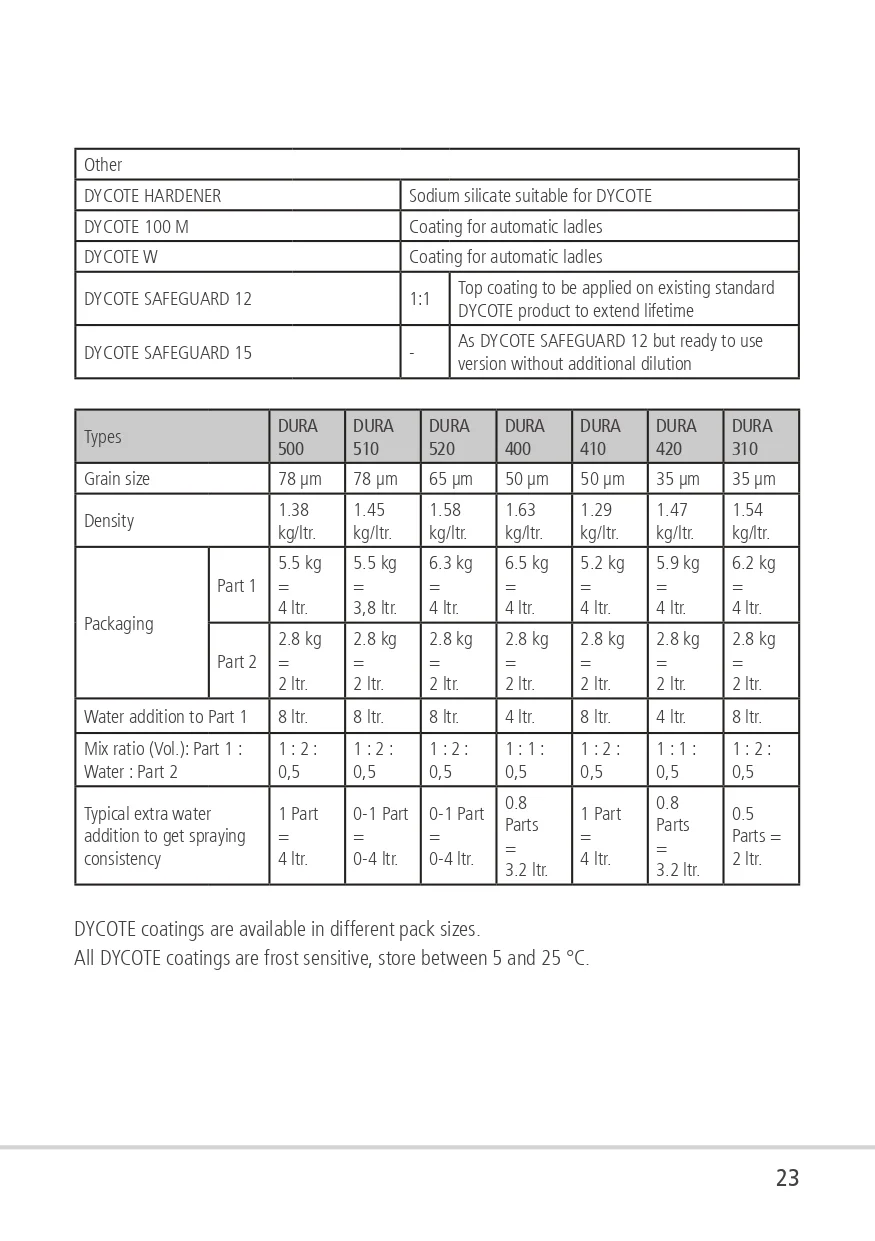
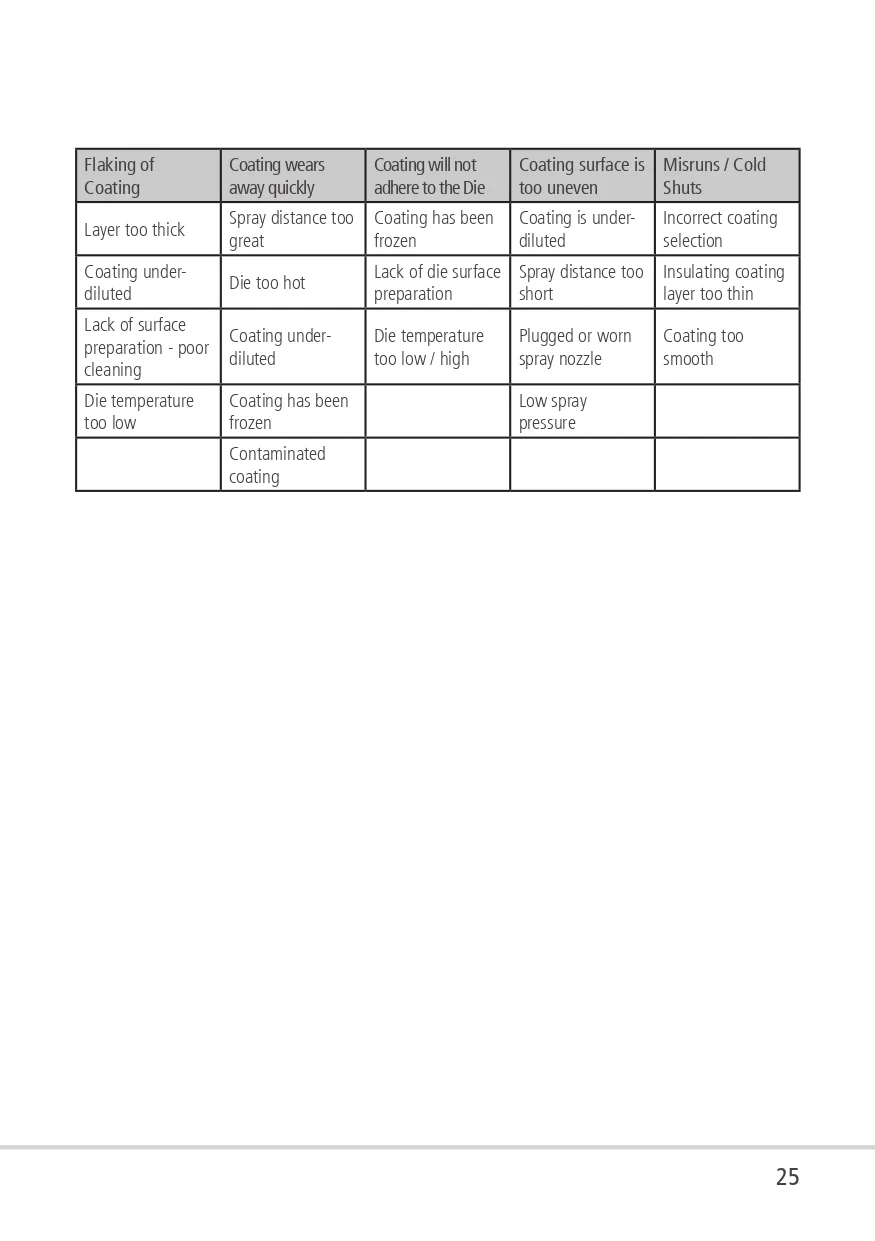
DYCOTE
Introduction
Although various aspects of the permanent mould casting process have been studied and developed, such as alloy selection, machine automation, etc., little attention has been given to the products and methods for preparing the surfaces of the die.
It is often the operator that selects and prepares the coating material, and the final choice is based almost exclusively on practical experience rather than technical and theoretical considerations. This manual aims to provide foundry engineers and operators involved in die preparation with the information required for the correct use of coating materials, in order to optimise efficiency and so improve foundry production.

Die casting and the role of coatings
Die casting is a process that uses permanent moulds made of metal (dies) enabling large batches of identical castings to be produced. Contrary to sand moulds, in which the permeability of the compacted sand allows the air to escape freely during casting, metal moulds are impermeable and therefore must be designed with suitable air vents. The advantages of the die process over sand are:
- Superior structural characteristics
- Better appearance of the casting
- Greater dimensional accuracy
- Reduced feed demand
- Higher production rates
- Lower cost (for larger batches)